Why Loneliness is the Next Public Health Emergency
Loneliness is no longer just a personal struggle—it’s a public health emergency. The U.S. Surgeon General declared loneliness an epidemic in 2023, warning that social isolation increases the risk of premature death by 26%. In fact, chronic loneliness is as harmful to health as smoking 15 cigarettes per day. The crisis is global, with impacts on individuals, workplaces, and entire economies.
Loneliness by the Numbers
- 1 in 4 adults worldwide report feeling lonely on a regular basis (WHO, 2023).
- In the U.S., nearly half of adults say they sometimes or always feel alone (Cigna, 2022).
- The UK appointed a Minister for Loneliness in 2018 after recognizing its societal costs.
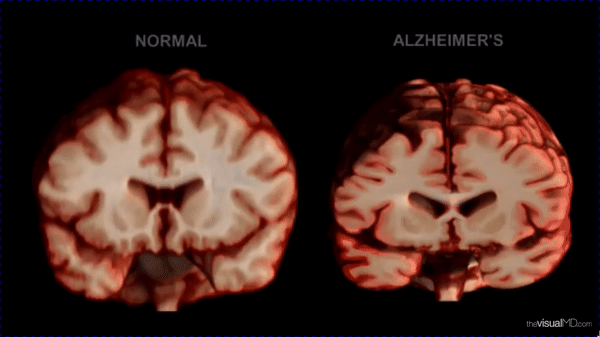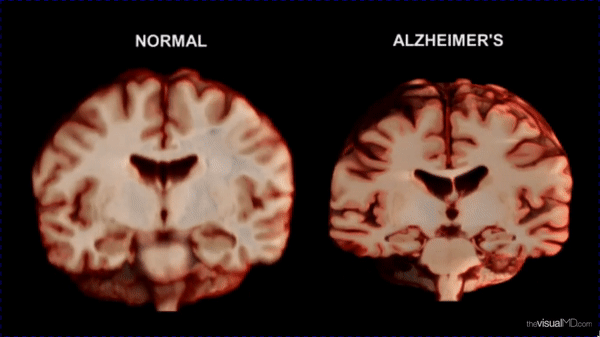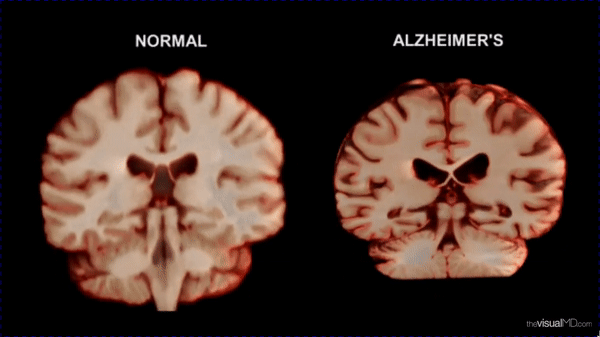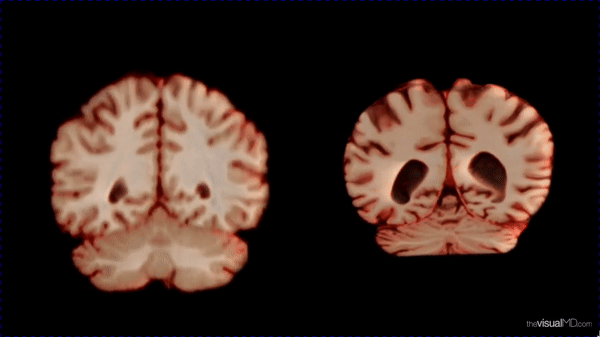
- Social isolation increases the risk of Dementia by 50%, heart disease by 29%, and stroke by 32% (CDC).
The Health Consequences
- Loneliness triggers chronic stress responses, weakening the immune system.
- It heightens risks of depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
- Socially isolated individuals have higher rates of hospitalization and longer recovery times.
- WHO notes that loneliness accelerates biological aging and cognitive decline.
Economic Impact
- Lost productivity due to loneliness costs U.S. employers up to $406 billion annually (Gallup, 2023).
- In Japan, Hikikomori (extreme social withdrawal) affects more than 1 million people and poses a long-term burden on healthcare and welfare systems.
- European Union studies show that socially isolated populations consume more health resources per capita.
Regional Perspectives
- United States: Declared loneliness an epidemic; increased funding for community-building programs.
- UK: National campaigns and ‘social prescribing’ initiatives encourage doctors to connect patients with social activities.
- Japan & South Korea: Rising suicide and isolation rates prompted the creation of state-led anti-loneliness policies.
- Middle East: Younger generations face loneliness despite large family structures, due to urbanization and digital overuse.
- India: Urban migration and digital addiction are creating a growing loneliness crisis among youth and elderly populations.
From Isolation to Connection
- Harvard’s long-term Adult Development Study shows that strong social connections are the single biggest predictor of long, healthy lives.
- WHO advocates for integrating social connection into public health priorities globally.
- Employers are recognizing that fostering belonging improves retention, creativity, and resilience.
- Innovations are emerging: community platforms, digital wellness solutions, and AI-driven social interventions.
What This Means for the Future
- Loneliness is not just an emotion—it’s a public health and economic issue with measurable costs.
- Governments, businesses, and wellness leaders must collaborate to address this silent epidemic.
- The future of mental wellness lies in solutions that measure, track, and actively reduce loneliness and isolation with real-world impact.
Loneliness is the epidemic of our time—but it doesn’t have to be. Join Basil Health’s mission to shape the future of measurable mental wellness.
Loneliness is no longer just a personal struggle—it’s a public health emergency. The U.S. Surgeon General declared loneliness an epidemic in 2023, warning that social isolation increases the risk of premature death by 26%. In fact, chronic loneliness is as harmful to health as smoking 15 cigarettes per day. The crisis is global, with impacts on individuals, workplaces, and entire economies.
Loneliness by the Numbers
- 1 in 4 adults worldwide report feeling lonely on a regular basis (WHO, 2023).
- In the U.S., nearly half of adults say they sometimes or always feel alone (Cigna, 2022).
- The UK appointed a Minister for Loneliness in 2018 after recognizing its societal costs.
- Social isolation increases the risk of dementia by 50%, heart disease by 29%, and stroke by 32% (CDC).
The Health Consequences
- Loneliness triggers chronic stress responses, weakening the immune system.
- It heightens risks of depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
- Socially isolated individuals have higher rates of hospitalization and longer recovery times.
- WHO notes that loneliness accelerates biological aging and cognitive decline.
Economic Impact
- Lost productivity due to loneliness costs U.S. employers up to $406 billion annually (Gallup, 2023).
- In Japan, hikikomori (extreme social withdrawal) affects more than 1 million people and poses a long-term burden on healthcare and welfare systems.
- European Union studies show that socially isolated populations consume more health resources per capita.
Regional Perspectives
- United States: Declared loneliness an epidemic; increased funding for community-building programs.
- UK: National campaigns and ‘social prescribing’ initiatives encourage doctors to connect patients with social activities.
- Japan & South Korea: Rising suicide and isolation rates prompted the creation of state-led anti-loneliness policies.
- Middle East: Younger generations face loneliness despite large family structures, due to urbanization and digital overuse.
- India: Urban migration and digital addiction are creating a growing loneliness crisis among youth and elderly populations.
From Isolation to Connection
- Harvard’s long-term Adult Development Study shows that strong social connections are the single biggest predictor of long, healthy lives.
- WHO advocates for integrating social connection into public health priorities globally.
- Employers are recognizing that fostering belonging improves retention, creativity, and resilience.
- Innovations are emerging: community platforms, digital wellness solutions, and AI-driven social interventions.
What This Means for the Future
- Loneliness is not just an emotion—it’s a public health and economic issue with measurable costs.
- Governments, businesses, and wellness leaders must collaborate to address this silent epidemic.
- The future of mental wellness lies in solutions that measure, track, and actively reduce loneliness and isolation with real-world impact.
Loneliness is the epidemic of our time—but it doesn’t have to be. Join BasilHealth’s mission to shape the future of measurable mental wellness.